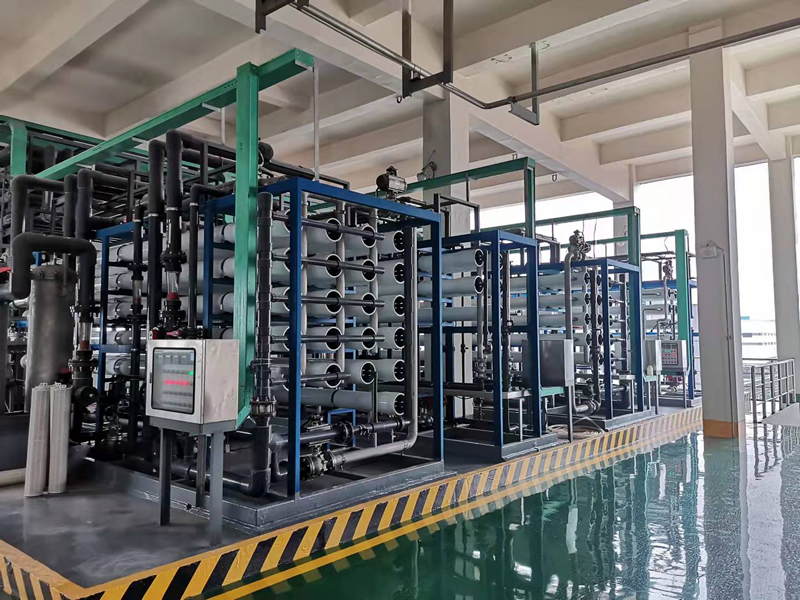
1. Significance of setting manual regulating valve and electric slow opening valve behind high-pressure pump
The design water yield of membrane element should be less than the standard water yield. If the standard water yield is used as the design water yield, the reverse osmosis membrane element will soon be polluted and damaged. According to the design guidelines provided by the membrane component manufacturer, it is recommended to select different design water production according to different water inlet sources. The feed pump that can ensure the design water production after 3 years should be selected, that is, the feed pump with higher pressure needs to be designed, but the design water production can be achieved without high pressure when the system is initially put into operation. Therefore, the feed pump pressure is abundant during the initial operation of the system, and with the passage of time, The pressure margin decreases gradually, so a manual regulating valve should be set behind the high-pressure pump to regulate the feed water pressure. Sometimes, the feed pump can be equipped with frequency conversion regulating device. At this time, the frequency conversion method can be used to adjust the feed water pressure. The manual regulating valve behind the high-pressure pump generally does not need to be adjusted frequently after setting. It is basically kept in a constant position for a period of time, and it is not necessary to open and close this valve every time the system is started. If there are no other valves behind the high-pressure pump, the high-pressure water source of the high-pressure pump will directly impact the membrane element every time the system is started, Especially when there is air in the system The phenomenon of "water hammer" is easy to cause the rupture of membrane elements. In order to prevent the above phenomena, an electric slow opening valve should be set behind the high-pressure pump, and the electric slow opening valve should be opened slowly after starting the high-pressure pump, that is, slowly loading pressure on the reverse osmosis membrane of the system. The electric slow opening valve should be a fully open and fully closed valve, and its fully open and fully closed time can be adjusted. Generally, it is set to 45 ~ 60s, so from the safety angle of reverse osmosis membrane elements The electric slow opening valve should be set in consideration of degree.
2. Automatic flushing function
After entering the reverse osmosis system, the feed water is divided into two ways. One way passes through the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane and becomes produced water, and the other way moves parallel along the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane and gradually concentrates. These concentrated water flows contain a large amount of salt, and even organic matter, colloid, microorganisms, bacteria and viruses. During the normal operation of the reverse osmosis system, the feed water / concentrated water flows along the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane at a certain flow rate, and these pollutants are difficult to deposit. However, if the reverse osmosis system stops running, these pollutants will immediately deposit on the surface of the membrane and pollute the membrane elements. Therefore, an automatic flushing system should be set in the reverse osmosis system to stop flushing the membrane element surface with clean water source to prevent the deposition of these pollutants.
3. The system is not flushed under pressure when starting up
For the system that has been used to add and stop protective agents, these protective agents shall be discharged, and then these protective agents shall be washed clean by non pressure flushing, and finally the system shall be started. For the system without adding and stopping protective agent, the system is generally filled with water at this time, but these water may have been stored in the system for a certain time. At this time, it is better to drain these water by non pressure flushing and then start up. Sometimes, the water in the system is not full. At this time, the air must be drained by non pressure flushing. If the air is not drained, it is easy to produce the phenomenon of "water hammer" and damage the membrane element.
4. Record of initial operation data
In the process of operation, due to the changes of system operating conditions, such as pressure, temperature, system recovery rate and feedwater concentration, the product water flow and quality will change. In order to effectively evaluate the performance of the system, it is necessary to compare the product water flow and quality data under the same conditions, because these data cannot always be obtained under the same conditions, Therefore, it is necessary to "standardize" the RO performance data under the actual operating conditions according to the constant operating conditions in order to evaluate the performance of RO membrane. The reference point of standardization is based on the operation data during initial operation (stable operation or after 24h), or the standard parameters of the reverse osmosis membrane element manufacturer. Standardization includes the "standardization" of product water flow and the "standardization" of salt transmittance.
5. The pH value of pretreatment is high, and the desalination rate of the system is too low as a whole
PH value is a measure of the pH value of water. The change of pH value will affect the balance of various ions in water, especially the balance of ions in carbonic acid system, and also affect the content of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. The desalination rate of reverse osmosis membrane for various ions is different, and its desalination rate will be significantly disturbed by pH value. Only when the pH value is between 6 ~ 8, the desalination rate is the highest. When the pH value is too high or too low, The desalination rate will be greatly reduced, and the pH value of lime softening pretreatment process often exceeds 1o, which will greatly reduce the desalination rate of the system.
6. Rupture of membrane element water production pipe
The user used an inappropriate lubricant during installation. The lubricant reacted with the central tube of the membrane element made of polymer material. At the same time, the central tube of the membrane element was broken due to the stress during installation. According to the suggestions of the membrane component manufacturer, petroleum lubricants (such as chemical solvent, Vaseline, lubricating oil and grease) are not allowed to be used to lubricate O-ring, connecting pipe, joint seal ring and concentrated water seal ring at any time. The only lubricants allowed are silicone glue, water or glycerol (glycerol).
7. Damage of FRP sheath of membrane element
During the installation, the corresponding gasket was not installed at the connection between the membrane element and the pressure vessel according to the manufacturer's requirements. At the same time, the electric slow door was not installed at the reverse osmosis inlet of the system, and the low-pressure flushing and exhaust were not carried out when the system was started, resulting in the instantaneous loading of high-pressure water supply to the membrane element, At the same time, due to the lack of low-pressure flushing and exhaust during system startup, the residual air cannot be discharged and compressed at the outlet end of the pressure vessel. Therefore, when the system is shut down, the membrane element is pushed back, causing the membrane element to move back and forth in the system.
8. Design principles of reverse osmosis system
Complete and accurate raw water analysis report must be provided before reverse osmosis system design. The water quality analysis report includes water quality type and main component indicators, and the required indicators include dissolved ions, silicon, colloid and organic matter (TOC).
8.1 typical dissolved anions
Bicarbonate (hc03 -), carbonate (CO32 -), hydroxyl (OH -), sulfate (SO42 -), chloride ion (Cl -), fluorine ion (F -), nitrate ion (NO3 -), sulfur ion (S2 -), phosphate (P044 -)
8.2 typical dissolved cations
Calcium ion (Ca2 +), magnesium ion (Mg2 +), sodium ion (Na +), potassium ion (K +), iron ion (Fe2 + or Fe3 +), manganese ion (Mn2 +), aluminum ion (Al3 +), barium ion (Ba2 +), copper ion (Cu2 +) and zinc ion (Zn2 +)
eight point three
The insoluble salts often encountered in reverse osmosis system are cas04, CaC03 and silicon. Other rarely encountered scaling include CaF2, BaS04 and srs04. Other ions that cause problems will be discussed below. Sulfate is abundant in most raw water, and their concentration is sometimes increased by manually adding sulfuric acid to adjust pH value. In this case, Ba + and Sr + ions should be analyzed and accurate to ppb and ppm, because the solubility of BaS04 and srs04 is lower than that of cas04, and they are difficult to re dissolve after scaling.
Alkalinity includes carbonate, bicarbonate and hydroxyl in negative ions. Alkalinity in natural water is mainly formed by HCO3 -. In water with pH below 8.3, bicarbonate and carbon dioxide exist in equilibrium. When the pH is higher than 8.3, hc03 - will be converted to CO32 - presence. If the pH of raw water reaches above 11.3, there will be 0h form. Carbon dioxide in the air will dissolve in water to form h2c03, and acid water will dissolve CaC03, which may be brought by flowing through CaC03 bearing rocks. The chemical dynamic equilibrium of CaC03 and Ca (hc03) 2 determined by pH in many natural water bodies is close to the saturation concentration. The solubility of Ca (hc03) 2 is greater than that of CaC03. If the raw water is concentrated in the RO system, CaC03 is easy to precipitate in the system. Therefore, adding scale inhibitor or adding acid to reduce pH value will often be used in RO system.
Nitrate: it is easy to dissolve in water, so it will not form precipitation in RO system. Nitrate is more closely related to health. When mammals, including humans, ingest nitrate, it will turn into nitrite, which will interfere with the combination of heme and oxygen in the blood and cause serious consequences, especially for fetuses and children. For this reason, the nitrate content in drinking water is required to be less than 40mg / L. The typical desalination rate of nitrate by reverse osmosis is 90-96%.
Iron and manganese: usually exist in the state of divalent dissolution in water or in the form of trivalent insoluble hydroxide. Fe2 + may come from the well water itself or from the corrosion of pumps, pipelines and water tanks, especially when acid is added to the upstream system. If the concentration of iron and manganese in raw water is greater than o.o5mg/l; It is oxidized to Fe (OH) 3 and Mn (OH) 2 by air or oxidant. When the pH value is high, precipitation will be formed in the system. The analysis shows that the existence of iron and manganese will accelerate the oxidative degradation of the membrane by oxidant, so iron and manganese must be removed in the pretreatment.
Aluminum: generally does not exist in dry natural water. Trivalent aluminum will form insoluble Al (OH) 3 in the RO system like ferric iron. When the pH is in the range of 5.3 to 8.5, Al2 (SO4) 3 and naal02 can be used for the pretreatment of surface water to remove the negative colloid in the water because of the high valence positive charge of aluminum. Be careful not to add too much aluminum salt, and the residual aluminum ion will pollute the membrane. FeCl3 and Fe (S04) 3 can also be used as coagulants instead of aluminum salts.
Copper and zinc: rarely found in natural water bodies. Sometimes trace amounts of copper and zinc in water come from pipe materials. In the range of pH value from 5.3 to 8.5, Cu (OH) 2 and Zn (OH) 2 are insoluble in water. Because their content in water is generally low, they will pollute the membrane system only when the system is not cleaned for a long time and they accumulate to a certain extent. However, if copper and zinc and oxidants (such as hydrogen peroxide) exist in the raw water at the same time, it will cause serious degradation of the membrane material.
Sulfide: dissolved in water in the form of H2S gas. Hydrogen sulfide can be removed by degassing unit or chlorine oxidation or air contact to become insoluble sulfur, which can be removed by multi-media filtration.
Phosphate: with strong negative electricity, it is easy to form insoluble salt with multivalent ions. The solubility of calcium phosphate is very limited when pH is neutral, and it is not high when pH is high. Adding scale inhibitor to the influent or reducing pH (less than 7) can prevent phosphate precipitation.
Silicon: it exists in most natural water bodies, and the concentration ranges from 1 to 100mg / L. And when pH is lower than 9.0, it mainly exists as Si (OH) 4. When pH is low, silicic acid can polymerize to form silicon colloid. When the pH is higher than 9.0, it will separate into sio32 ions and form precipitation with calcium, magnesium, iron or lead. Silicon and silicate precipitates are difficult to dissolve. Hydrogen fluoride amine solution is more effective in cleaning silicon scale, but the discharge of hydrogen fluoride amine solution will cause environmental pollution. When the silicon content in the influent exceeds 20mg / L, pay attention to the potential danger of silicon scaling.
Colloid (suspended solids) analysis: sludge density index (SDI), also known as pollution index (FI), is an important index to balance the potential pollution of colloid (particles) in RO influent. The colloids in RO influent are various, often including bacteria, clay, silica colloid and iron corrosion products. Some chemicals such as Mingji, ferric chloride or cationic polymerization agent will be used in the clarifier in pretreatment to remove colloidal pollution or through subsequent medium filter.
Total bacterial count and organic content: there are two methods to determine the number of bacteria in water, one is culture method, the other is fluorescence staining method, which is more commonly used because it is very convenient and fast. The organic matter in raw water is generally oil surfactant, water-soluble polymer and humic acid. The detection indexes include total organic carbon (TOC), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). In order to analyze organic compounds more accurately, liquid chromatography and GC-MS are needed. If the TOC content in raw water is greater than 3mg / L, the pretreatment unit shall consider the process of removing organic matter.